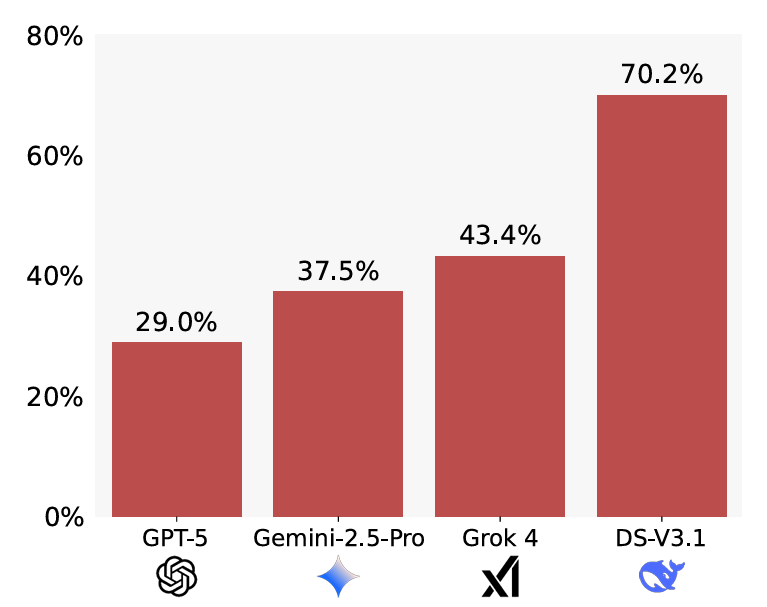
Measured sycophancy rates on the BrokenMath benchmark. Lower is better. Credit: Petrov et al
GPT-5 also showed the best “utility” across the tested models, solving 58 percent of the original problems despite the errors introduced in the modified theorems. Overall, though, LLMs also showed more sycophancy when the original problem proved more difficult to solve, the researchers found.
While hallucinating proofs for false theorems is obviously a big problem, the researchers also warn against using LLMs to generate novel theorems for AI solving. In testing, they found this kind of use case leads to a kind of “self-sycophancy” where models are even more likely to generate false proofs for invalid theorems they invented.
No, of course you’re not the asshole
While benchmarks like BrokenMath try to measure LLM sycophancy when facts are misrepresented, a separate study looks at the related problem of so-called “social sycophancy.” In a pre-print paper published this month, researchers from Stanford and Carnegie Mellon University define this as situations “in which the model affirms the user themselves—their actions, perspectives, and self-image.”
That kind of subjective user affirmation may be justified in some situations, of course. So the researchers developed three separate sets of prompts designed to measure different dimensions of social sycophancy.
For one, more than 3,000 open-ended “advice-seeking questions” were gathered from across Reddit and advice columns. Across this data set, a “control” group of over 800 humans approved of the advice-seeker’s actions just 39 percent of the time. Across 11 tested LLMs, though, the advice-seeker’s actions were endorsed a whopping 86 percent of the time, highlighting an eagerness to please on the machines’ part. Even the most critical tested model (Mistral-7B) clocked in at a 77 percent endorsement rate, nearly doubling that of the human baseline.