Campylobacter is a common cause of food poisoning and is on the rise in Michigan and around the world. It spreads to humans through food products made from, or that come into contact with, infected animals, primarily chickens and other birds. So far, only one outbreak of campylobacteriosis has been definitively linked to feces from wild birds. Still, because it causes milder symptoms than some other types of bacteria, the Centers for Disease Control considers campylobacter a significantly underreported cause of food-borne illness that may be more common than current data indicates.
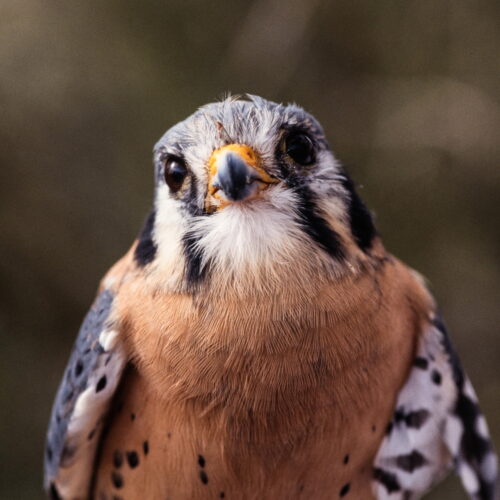
“Trying to get more birds of prey would be beneficial to farmers,” Smith said. “If you have one predator, versus a bunch of prey, you have fewer birds overall. If you have a lot fewer birds, even if the ones that are there are carrying bacteria, then you can reduce the transmission risk.”
The study’s findings that kestrels significantly reduce physical damage and food safety risks on Michigan cherry farms demonstrate that managing crops and meeting conservation goals—by bolstering local kestrel populations and eliminating the need to clear wildlife habitat around agricultural areas—can be done in tandem, study authors say. They recommend farmers facing pest-management issues consider building kestrel boxes, which cost about $100 per box and require minimal maintenance.
Whether nesting boxes in a given region will be successfully inhabited by kestrels depends on whether there is an abundance of the birds there. In Michigan’s cherry-growing region, kestrels are so abundant that 80 percent to 100 percent of boxes become home for kestrels rather than other nesting birds, said Catherine Lindell, avian ecologist at Michigan State University and senior author of the study.
“It seems like this is just a great tool for farmers,” Lindell said, suggesting interested farmers “put up a couple boxes and see what happens.”
K.R. Callaway is a reporter and editor specializing in science, health, history, and policy stories. She is currently pursuing a master’s degree in journalism at New York University, where she is part of the Science, Health, and Environmental Reporting Program (SHERP). Her writing has appeared in Scientific American, Sky & Telescope, Fast Company and Audubon Magazine, among others.
This story originally appeared on Inside Climate News.